House centipedes are fascinating creatures that often invoke a sense of curiosity and even a bit of fear. These elongated arthropods, with their numerous legs and lightning-fast movements, are commonly found in homes and buildings. But have you ever wondered about their behavior patterns? Do house centipedes travel in pairs?
In this article, we will explore the intriguing world of house centipedes and uncover the truth behind their travel habits. From their characteristics and behavior to their life cycle and distribution, we will delve into the fascinating aspects of these creatures. Additionally, we will provide useful tips on how to manage and prevent house centipede infestations, ensuring a peaceful and pest-free home environment.
So, if you’ve ever been curious about the mysterious behavior of house centipedes or want to learn effective techniques to keep them at bay, read on to find the answers you seek. Let’s dive deep into the intriguing world of house centipedes and discover the truth behind their solitary or paired travels.
Characteristics and Behavior of House Centipedes
House centipedes are fascinating creatures with unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding these aspects can help you better coexist with these beneficial arthropods.
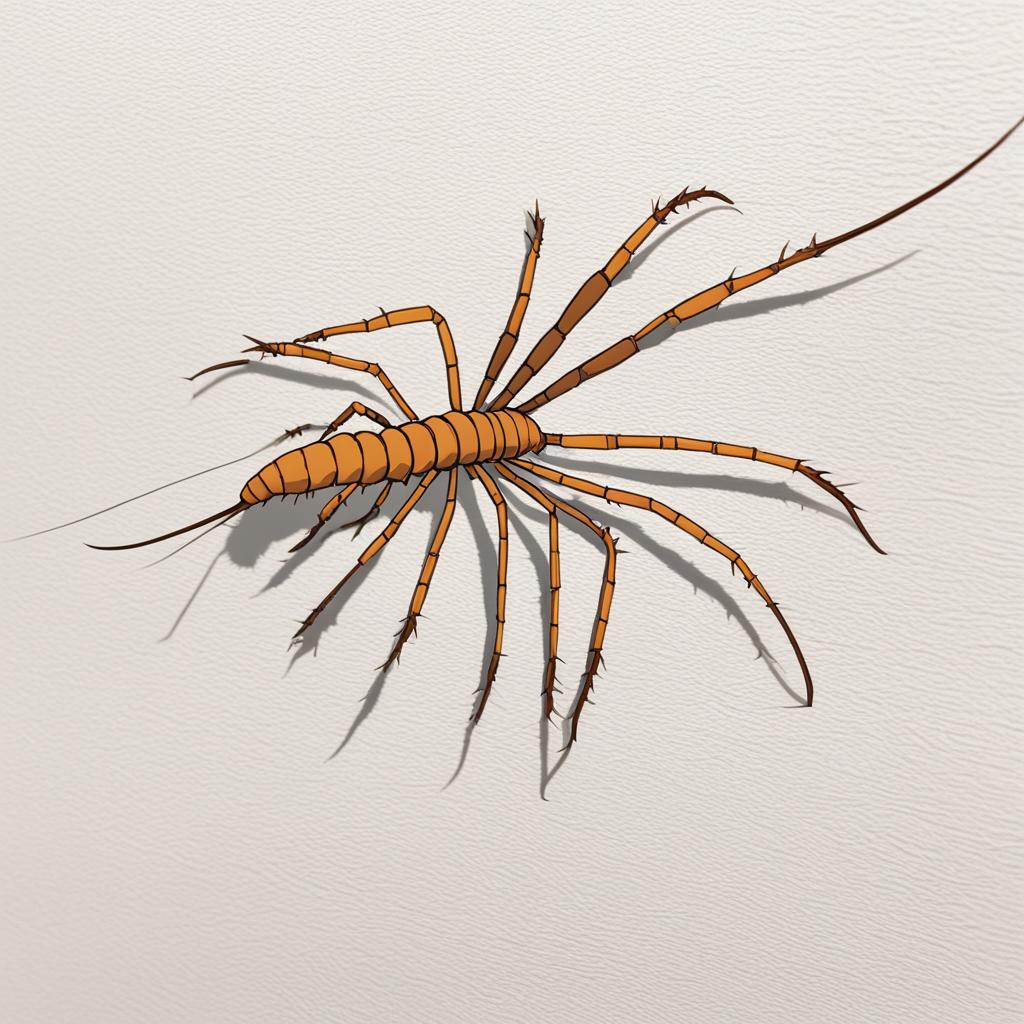
House centipedes have flat, elongated bodies and come in a range of sizes, varying from 1/6 inches to 6 1/2 inches in length. They possess an odd number of leg pairs, with the number of pairs depending on the species, ranging from 15 to 177. These numerous legs contribute to their quick and agile movements, allowing them to navigate various terrains with ease.
The color patterns of house centipedes can vary, but the most common ones showcase greyish-yellow bodies with three distinctive dark stripes. These patterns provide effective camouflage, helping them blend into their surroundings and avoid predation.
House centipedes are typically found in damp and cool places such as basements, bathrooms, and crawl spaces. These environments provide the necessary moisture for their survival and reproductive success. By thriving in these habitats, they can access a steady supply of prey and fulfill their role as active hunters.
Speaking of prey, house centipedes feed on a variety of arthropods, including silverfish, roaches, spiders, moths, flies, and termites. Their voracious appetite and constant search for prey make them excellent natural pest control agents. By preying on these common household pests, house centipedes help maintain a balanced ecosystem within your home.
Overall, the behavior of house centipedes revolves around their hunting and survival instincts. They are nocturnal creatures, primarily active during the night when their prey is most active as well. Their unique adaptations, such as the numerous legs and elongated bodies, enable them to navigate tight spaces and hunt effectively.
In summary, house centipedes possess distinctive physical characteristics, ranging from their elongated bodies and numerous leg pairs to their characteristic color patterns. They prefer damp and cool habitats, where they actively hunt and feed on various arthropod pests. Understanding their behavior and ecological role can help foster a harmonious cohabitation with these beneficial creatures.
Life Cycle and Distribution of House Centipedes

House centipedes, despite their creepy appearance, go through a fascinating life cycle before reaching maturity. Let’s explore their development and discover where these creatures can be found.
Life Cycle of House Centipedes
House centipedes undergo a series of molts and stages as they grow. They start as eggs, which are laid by adult females in warm and humid locations. After hatching, the house centipede larvae emerge and go through six larval instars or molts. Each molt brings them closer to adulthood, with their bodies and legs gradually elongating.
Once the larval stage is complete, the house centipedes enter the post-larval stage. During this period, they go through four instars, continuing to grow and develop. The time it takes for a house centipede to reach maturity can vary, but it generally ranges from several months to a year, depending on factors like food availability and environmental conditions.
Female house centipedes have an impressive reproductive capacity. They can live for several years and produce up to 150 offspring over their lifetime. This high reproductive rate allows house centipede populations to persist and thrive in suitable habitats.
Distribution of House Centipedes
House centipedes are native to the Mediterranean region but have expanded their distribution to different parts of the world. They have also become common in the United States, particularly in the southern states. The accidental introduction of these creatures to new areas has contributed to their widespread presence.
While house centipedes prefer the shelter and abundance of small prey found inside homes, they can also be encountered outdoors. During the summer months, they may be found in areas near buildings, such as gardens, porches, and basements. However, they do not survive winters in colder regions and seek heated structures where they can reproduce and thrive.
To get a visual of the distribution of house centipedes, take a look at the map below:
| Region | Distribution |
|---|---|
| Mediterranean | Native range |
| United States | Southern states |
| Worldwide | Accidental introductions |
As seen in the table and image, house centipedes have established a presence in various parts of the world, mainly due to human activities and their adaptability to indoor environments.
Managing and Preventing House Centipede Infestations
To manage the house centipede population in your home, there are several strategies you can employ. By reducing their food sources and modifying their habitat, you can effectively control and prevent infestations. Here are some helpful tips:
- Control other insect and spider populations: Since house centipedes primarily feed on other arthropods, reducing their prey sources can significantly impact their population. Implement integrated pest management practices to manage pest insects and spiders in your home. This can include using sticky insect traps to identify the types of arthropods that serve as a meal for the centipedes.
- Harborage reduction: House centipedes seek shelter in cracks, crevices, and other hiding spots. Seal these entry points by caulking cracks and gaps in concrete slabs and block walls. By eliminating potential harborage areas, you make the environment less attractive to centipedes.
- Reduce humidity: House centipedes thrive in damp and humid conditions. Use dehumidifiers and fans to lower the humidity levels in your home, especially in areas prone to moisture buildup such as basements and bathrooms. Additionally, ensure proper grading around the perimeter of your home to facilitate water movement away from the foundation.
- Extermination methods: If the house centipede population is already a persistent problem, you may consider using insecticides for extermination. There are different types of insecticides available, including emulsifiable concentrates, wettable powders, and dusts. However, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety precautions when using pesticides.
- Prevention tips: Taking proactive measures to prevent house centipede infestations is crucial. Here are some additional prevention tips:
- Reduce moisture levels in your home by fixing water leaks and using dehumidifiers.
- Remove clutter in basements, attics, and crawlspaces to eliminate hiding places for centipedes.
- Eliminate food sources by controlling other pest populations and practicing good sanitation.
- Seal entryways by repairing cracks and gaps, and install weather stripping on doors and windows.
- Create a barrier around the perimeter of your home using insecticides to prevent centipedes from entering.
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Control other insect and spider populations | By reducing the centipedes’ prey sources, their population can be effectively managed. |
| Harborage reduction | Sealing cracks and crevices eliminates hiding spots for centipedes. |
| Reduce humidity | Lowering humidity levels in your home makes it less conducive for centipede survival. |
| Extermination methods | Using insecticides can help eliminate existing centipede populations. |
| Prevention tips | Taking preventive measures can help avoid future centipede infestations. |
By following these strategies, you can effectively manage and prevent house centipede infestations in your home. Remember, it is important to be persistent and consistent with your efforts to ensure long-term success in controlling these pests.
Tips for Preventing Future House Centipede Problems
To prevent future house centipede problems, there are several steps you can take to ensure a centipede-free home environment. Here are some practical tips to help you keep these unwanted pests at bay:
- Reduce Moisture: House centipedes thrive in damp environments, so it’s essential to control moisture levels in your home. Repair any water leaks promptly, use dehumidifiers in high-humidity areas, and run exhaust fans to keep the air circulating.
- Remove Clutter: Centipedes love to hide in cluttered areas like basements, attics, and crawlspaces. Declutter these spaces to limit their hiding places and make them less attractive to centipedes.
- Eliminate Food Sources: Centipedes feed on other insects and spiders, so controlling these populations will help eliminate their food source. Regularly clean up crumbs, fix any gaps or cracks where pests can enter, and consider using natural pest repellents to deter insects.
- Seal Entryways: Centipedes can enter your home through tiny cracks and gaps. Inspect your home for entry points and seal them by repairing cracks, adding weather-stripping to doors and windows, and installing screens on windows and vents.
- Create a Barrier: Applying insecticides around the perimeter of your house can create a barrier that prevents centipedes from entering. Choose insecticides specifically designed for centipede control and follow the instructions carefully to maintain a safe and effective barrier.
By following these tips, you can minimize the chances of a house centipede infestation and enjoy a centipede-free home environment. Remember, prevention is key in keeping these natural insect hunters at bay.
FAQ
Q: Do house centipedes travel in pairs?
A: No, house centipedes do not travel in pairs. They are solitary creatures and prefer to live and hunt alone.
Q: What are the characteristics and behavior of house centipedes?
A: House centipedes have flat, elongated bodies with 15 pairs of legs. They can range in size from 1/6 inches to 6 1/2 inches long. They have greyish-yellow bodies with three dark stripes. House centipedes are usually found in damp and cool places like basements, bathrooms, and crawl spaces. They are active hunters and feed on silverfish, roaches, spiders, moths, flies, and termites.
Q: What is the life cycle and distribution of house centipedes?
A: House centipedes go through six larval instars or molts before reaching maturity. After the larval stage, they go through four post-larval instars. Female house centipedes can survive for several years and produce up to 150 young. House centipedes are native to the Mediterranean region but have spread throughout the United States and the world. During the summer, they may also be found outdoors in areas near buildings.
Q: How can I manage and prevent house centipede infestations?
A: To manage a house centipede population, it is important to reduce their food source by controlling other insect and spider populations in the house. Harborage reduction is also effective, which involves sealing cracks and crevices in concrete slabs and block walls. Reducing humidity with dehumidifiers and grading the soil around the building to facilitate water movement away from the foundation can also help. Insecticides can be used for extermination, with options including emulsifiable concentrates, wettable powders, and dusts. Proper safety precautions should be followed when using pesticides.
Q: What are some tips for preventing future house centipede problems?
A: To prevent future house centipede problems, it is important to control moisture levels in the house by repairing water leaks, using dehumidifiers, and running exhaust fans in high-humidity areas. Removing clutter in basements, attics, and crawlspaces will limit their hiding places. Controlling other insect and spider populations will eliminate the food source for centipedes. Sealing entryways by repairing cracks and gaps, as well as adding weather stripping to doors and windows, will prevent centipedes from getting inside. Creating a barrier with insecticides around the perimeter of the house can also help keep unwanted pests out.
